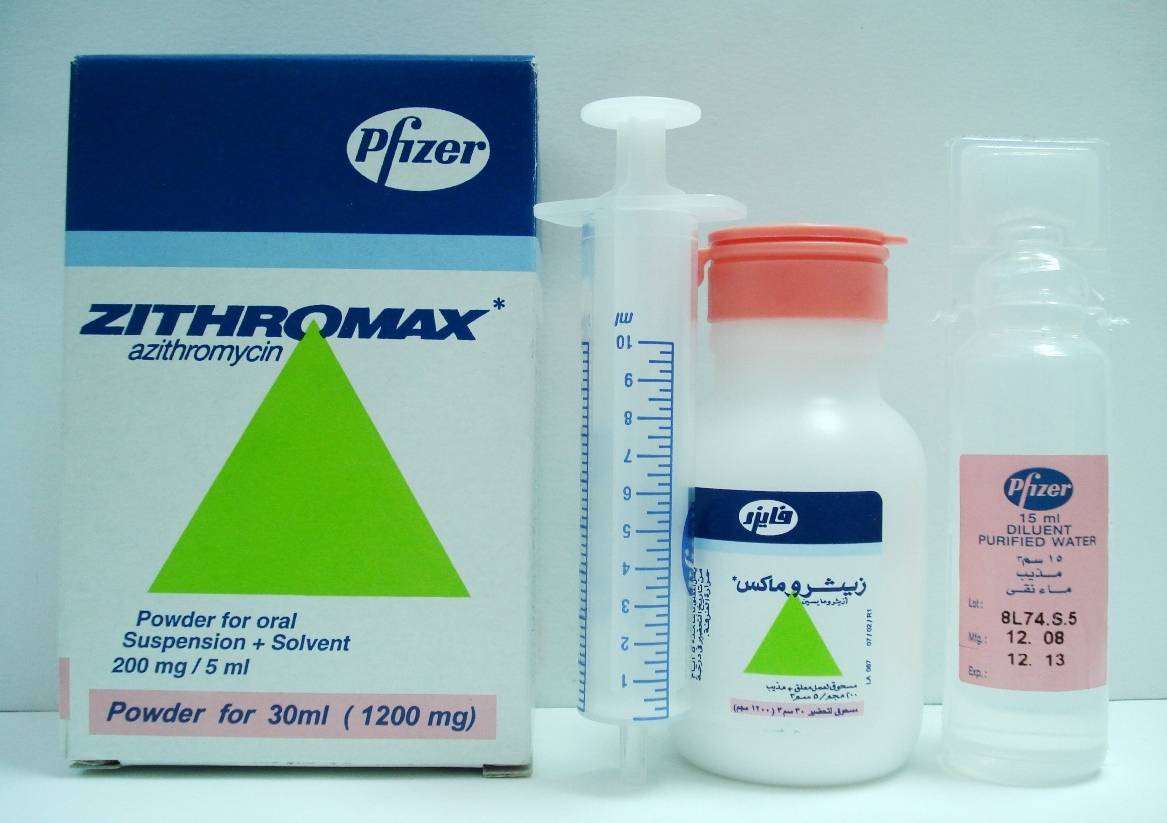
Zithromax Syrup is a prescription antibiotic containing azithromycin as its active ingredient. This broad-spectrum macrolide antibiotic is formulated in a palatable suspension form, making it particularly suitable for children and adults who have difficulty swallowing tablets.
Uses
Zithromax Syrup effectively treats various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, skin infections, ear infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections. It’s particularly effective against community-acquired pneumonia and bronchitis.
Benefits
- Provides rapid infection control
- Requires shorter treatment duration
- Offers convenient once-daily dosing
- Shows excellent tissue penetration
- Maintains therapeutic levels for extended periods
- Features good taste for better compliance
- Demonstrates broad-spectrum activity
- Shows effectiveness against resistant bacteria
How It Works
Azithromycin works by binding to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes, preventing protein synthesis necessary for bacterial growth. This bacteriostatic action ultimately leads to bacterial cell death and infection clearance.
Dosage
| Age Group | Recommended Dosage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Adults | 500mg | Once daily for 3 days |
| Children >6 months | 10mg/kg | Once daily for 3 days |
| Children <6 months | As prescribed | As directed |
Warnings
Discontinue use and seek immediate medical attention if experiencing severe allergic reactions, severe diarrhea, or irregular heartbeat. Not suitable for patients with liver disease without close monitoring.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Zithromax Syrup include gastrointestinal disturbances, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Less frequent effects may include headache, dizziness, or temporary changes in taste sensation.
Warning
Discontinue use and seek immediate medical attention if experiencing severe allergic reactions, severe diarrhea, or irregular heartbeat. Not suitable for patients with liver disease without close monitoring.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Generally considered safe during pregnancy (Category B). Can be used while breastfeeding, but monitor infant for potential side effects. Consult healthcare provider before use.
Interactions
- May interact with antacids
- Could affect warfarin effectiveness
- Possible interaction with digoxin
- May influence certain heart medications
- Can interact with ergot derivatives
Precaution
Take on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after meals). Complete the full course even if symptoms improve. Shake well before each use. Keep follow-up appointments for monitoring if prescribed.
Important Information
Store Zithromax Syrup at room temperature below 30°C. Keep tightly closed and protect from light. Shake well before each use. Complete full prescribed course even if feeling better. Refrigeration not required after reconstitution. Use within 10 days after mixing. Do not share antibiotics with others. May cause QT interval prolongation in susceptible patients. Report any unusual symptoms to healthcare provider.
Product Image Highlights



Customer questions & answers
There are no questions yet. Be the first to ask a question about this product.
Selected with Care, Just for You
-
 ₦4,000.00Rated 0 out of 5
₦4,000.00Rated 0 out of 5Loxagyl Suspension effectively treats various infections in children, including anaerobic...
-
 ₦5,500.00Rated 0 out of 5
₦5,500.00Rated 0 out of 5Levotex tablets contain 500mg of levofloxacin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic used...
-
 ₦4,000.00Rated 0 out of 5
₦4,000.00Rated 0 out of 5Barbiclox Suspension is used to treat bacterial infections like bronchitis,...
-
 ₦5,000.00Rated 0 out of 5
₦5,000.00Rated 0 out of 5Donyflox-500mg is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory...




















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.